The Chernobyl disaster was one of the worst nuclear accidents in history.
It occurred on April 26, 1986, at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine, then part of the Soviet Union.
A series of human errors and design flaws caused a massive explosion and fire that released large amounts of radioactive material into the atmosphere.
The consequences were devastating for people, animals, and the environment.
What Happened at Chernobyl?
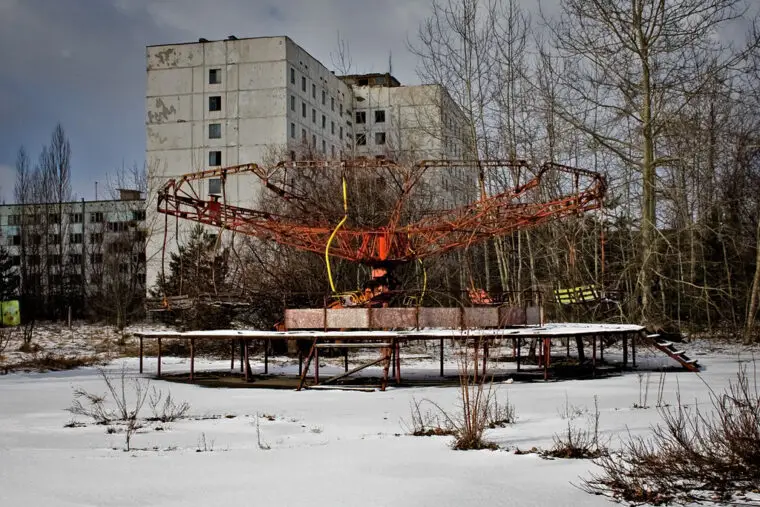

The Chernobyl disaster happened during a safety test at reactor number four.
The test was meant to simulate a power outage and check if the backup generators could provide enough electricity to keep the cooling pumps running.
However, several mistakes were made during the test preparation and execution:
- The power level of the reactor was reduced too much, making it unstable.
- The emergency safety systems were turned off or bypassed to prevent them from interfering with the test.
- The control rods that regulate the nuclear fission reaction were pulled out too far, creating a power surge.
At 1:23 am on April 26, 1986, two powerful explosions blew off the roof of the reactor building and exposed the burning graphite core to the air.
The fire sent a plume of radioactive smoke and dust into the sky that spread over Europe and beyond.
What Were the Effects of Chernobyl?
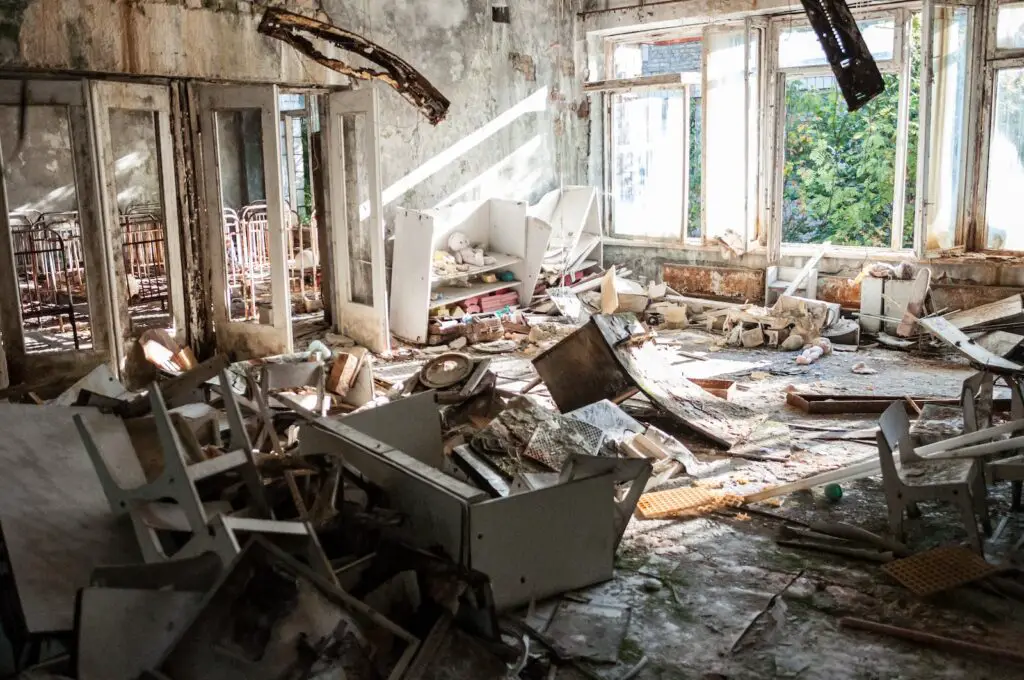

The effects of Chernobyl were catastrophic for human health and the environment. Here are some of them:
- More than 30 workers and firefighters died within months from acute radiation sickness.
- About 116,000 people were evacuated from the nearby town of Pripyat and other affected areas.
- An exclusion zone of about 2,600 square kilometers (1,000 square miles) was established around the plant where access is restricted.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ldYeFLZqh3Q
- Thousands of people developed thyroid cancer and other diseases from exposure to radioactive iodine.
- Millions of people in Ukraine, Belarus, Russia, and other countries were exposed to low levels of radiation that increased their risk of cancer and other health problems.
- Wildlife populations declined in some areas due to radiation effects but also recovered in others due to reduced human activity.
- The contaminated land and water posed long-term challenges for agriculture, forestry, fishing, and tourism.
Why Does Chernobyl Matter Today?
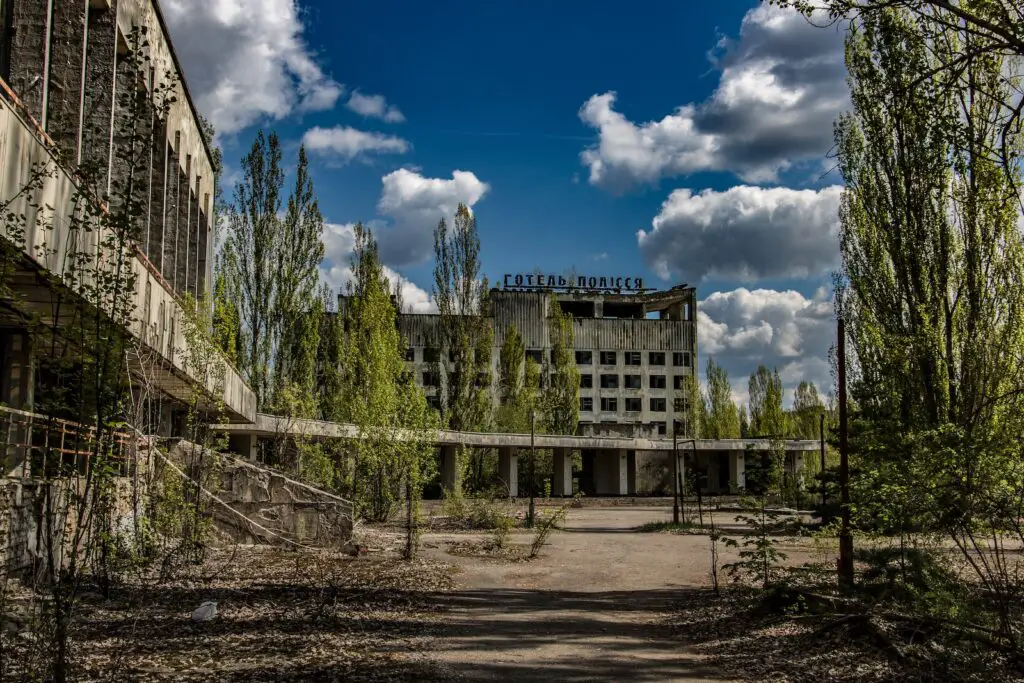

The Chernobyl disaster is still relevant today for several reasons:
- It is a reminder of the potential dangers of nuclear power if not managed safely and responsibly.
- It is a case study of how human error , poor communication , lack of transparency , and political pressure can lead to disaster .
- It is an example of how international cooperation , scientific research , humanitarian aid , and public awareness can help mitigate the consequences .
- It is an inspiration for artistic expression , cultural memory , environmental activism , and social justice .
Conclusion
FAQ
Q: When did Chernobyl happen?
A: The Chernobyl disaster happened on April 26, 1986.
Q: Where is Chernobyl located?
A: Chernobyl is located in northern Ukraine, near the border with Belarus.
Q: How many people died because of Chernobyl?
A: The exact number of deaths caused by Chernobyl is hard to estimate, but some sources suggest that up to 4, 000 people died from radiation-related illnesses in the years following the accident.
Q: Is Chernobyl safe to visit now?
A: Parts of the exclusion zone around Chernobyl are open to visitors with official permission and guides . However , there are still areas with high levels of radiation that are dangerous and off-limits . Visitors should follow safety rules and respect the site as a place of tragedy .

I am a fun fact enthusiast and creator of Facts On Tap.
I love to share my knowledge and curiosity with readers and inspire them to learn something new every day.
When I’m not writing, I enjoy traveling, reading, and playing trivia games with my friends.